New Delhi: Imagine going to see your doctor only to be told that they don’t know what is happening to your body, what your disease is. Imagine they can diagnose your disease but tell you that there is no cure or even treatment available. Or that the treatment available is not fully effective but just the best possible option. You are totally blank thereafter while thinking how the disease will affect you, your work, your family and your life.
70 million people in India and approx 350 million around the world suffer from rare diseases, claims Indian Society for Clinical Research.
There are 7,000 known rare diseases, most of which are progressive, life-threatening and chronically debilitating conditions and out of them, the treatment is available for just 500 diseases.
This is the reality for many rare disease patients like Sachin, an 18 year old boy, who suddenly suffered from a rare disease. He and his family never thought that a simple Knot one day will turn out to be a serious problem for them.
“A knot which he had on his head was not a simple knot. We discovered the disease connected with the knot, when suddenly one day a lot of blood started flowing out of his head. After MRI and angiogram test when doctor told that Sachin had AVM, which affects less than 1% of the population, was a big shock for us,” says his father, Jaiveer Singh.
What is AVM?
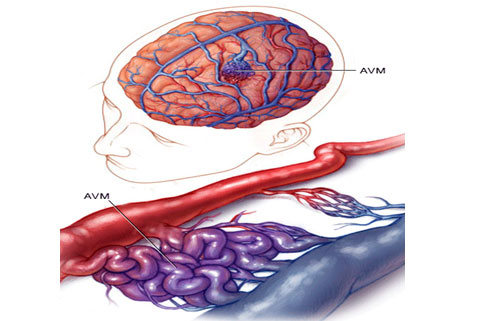
AVM stands for Arteriovenous Malformation. An AVM is a tangle of abnormal and poorly formed blood vessels (arteries and veins). They have a higher rate of bleeding than normal vessels.
The arteries are responsible for taking oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the brain. Veins carry the oxygen-depleted blood back to the lungs and heart. A brain AVM disrupts this vital process.
Normally, arteries carry blood containing oxygen from the heart to the brain, and veins carry blood with less oxygen away from the brain and back to the heart. When an arteriovenous malformation (AVM) occurs, a tangle of blood vessels in the brain or on its surface bypasses normal brain tissue and directly diverts blood from the arteries to the veins.

An arteriovenous malformation can develop anywhere in your body but occurs most often in the brain or spine. Even so, brain AVMs are rare and affect less than 1 percent of the population and estimates shows that about one in 2,000–5,000 people may have an AVM. AVMs are more common in males than in females.
AVMs are considered as dangerous because of the fact that it can damage the brain or spinal cord through three basic mechanisms: by reducing the amount of oxygen reaching neurological tissues; by causing bleeding (haemorrhage) into surrounding tissues; and by compressing or displacing parts of the brain or spinal cord.
A brain AVM contains abnormal and, therefore, “weakened” blood vessels that direct blood away from normal brain tissue. These abnormal and weak blood vessels dilate over time. Eventually they may burst from the high pressure of blood flow from the arteries, causing bleeding into the brain.The chance of a brain AVM bleeding is 1 percent to 3 percent per year. Over 15 years, the total chance of an AVM bleeding into the brain — causing brain damage and stroke — is 25 percent.
Functions which an AVM affect:
• The frontal lobe functions to process motor (movements), and frontal eye fields, regulates personality and articulation (and other aspects) of speech.
• The parietal lobe functions to process sensory information, such as interpretation of pain and temperature, light touch, vibration and more.
• The temporal lobe functions to process things related to hearing, memory, learning and receptive speech.
• The occipital lobe functions to process things related to vision.
Why and When AVMs occurs?
Possible answer to why and when brain AVMs occurs is difficult to give as the cause of AVMs still not properly clear. Most people are born with them, but they can occasionally form later in life. AVMs are rarely passed down among families genetically.
Dr. Ashish Pitale says, “AVMs can appear at any age, but as these abnormalities tendto result from a slow buildup of neurological damage over time, they are most often noticed when people are in their 20s, and 30s. With the time, AVM had serious physical outcomes like failure to thrive and congestive heart failure. And, these symptoms worsen in; pregnant women especially due to increase in blood pressure and children’s who born with this condition areoften remain developmentally impaired.”
People with brain AVMs experience signs and symptoms:
• More than 50 percent of patients with an AVM have an intracranial hemorrhage ( type of bleeding that occurs inside the skull)
• Among AVM patients, 20 percent to 25 percent have focal or generalized seizures (stoke).
• Patients may have localized pain in the head due to increased blood flow around an AVM.
• Fifteen percent may have difficulty with movement, speech and vision also.
Other signs of AVMs are:
• Weakness in the legs or arms
• Paralysis
• Sudden onset of a severe headache, vomiting, stiff neck
• Migraine
• Bruit: an abnormal swishing or ringing sound in the ear caused by blood pulsing through the AVM
Treatment:
AVMs can’t be prevented. However, you can manage and treat symptoms with proper medical care. They are diagnosed through tools such as CT scan, MRI, Angiography and Magnetic Resonance Angiogram.
On the other hand, treatment to AVMs will depend on age, condition, and physical health. It can be treated both ways through medication as well as surgery also depending on the type, symptoms, and location of the AVM.
Taking prescribed medications can help avoid bleeding problems, pain, and other complications.Whereas,Surgery to repair or remove damaged blood vessels includes three options:
• conventional surgery
• endovascular embolization (involves the injection of non-reactive liquid adhesive material into AVM in order to block it off)
• radiosurgery (surgery using radiation)
Although, the chances of completely curing an AVM disease is about 20% only and Certain types of AVM are more suitable for embolization and have a much higher cure rate.
Lastly, Rare Disease Facts:
• A disease that is found in less than 6.5-10 per 10,000 people is defined as a rare disease by World Health Organisation.
• 1 in 20 Indians is affected by a rare disease.
• 80% of the rare diseases have a genetic origin
• 50% rare diseases affect children, most of who do not live beyond five years.
• There are still no known cures for most rare diseases, and the cost of treatment is extremely high.
Therefore, noticed on the last day of February every year; rare disease day is observed in about 80 countries including India, which aims to raise awareness among people about unknown diseases and their impact.
We need to create more awareness about rare diseases and impress upon the government the need to focus on them to come with solutions.
References:
www.mayoclinic.org
www.strokeassociation.org
www.healthline.com
www.mayfieldclinic.com
